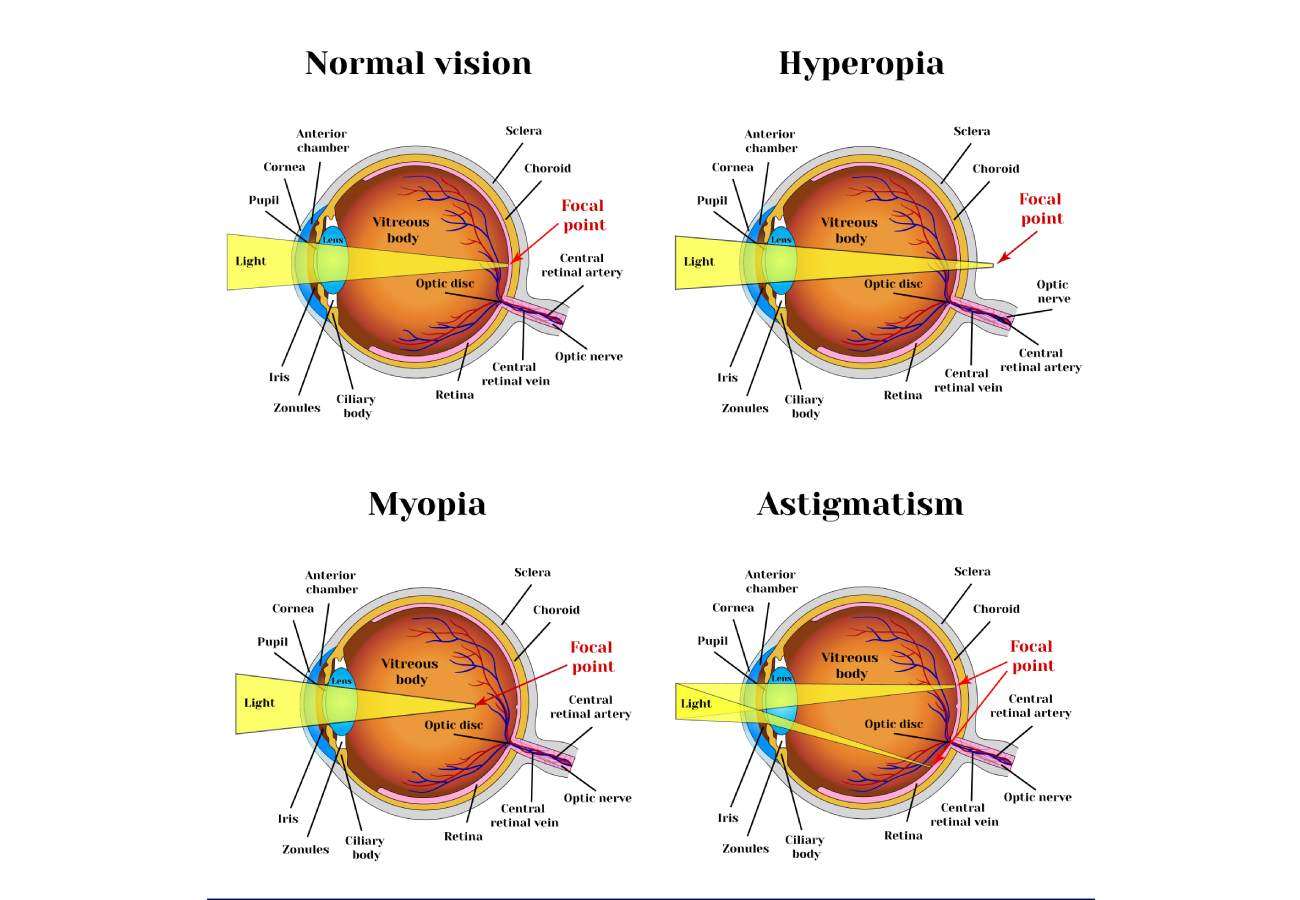
In emmetropic eyes, light rays from objects pass through the cornea, crystalline, are projected onto a point on the retina and finally it is sent to the brain through the optic nerve where the image is formed. Ocular refraction is the measurement of the entry of light rays into the eye and the calculation of its deviation and measures the visual acuity of a person.
Through ocular refraction we can measure the type of refractive defect What does a patient have? myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism o presbyopia. In Área Oftalmológica Avanzada We explain below what is ocular refraction and what pathologies it helps to detect.

What is the eye refraction test?
Ocular refraction is the study of how light rays penetrate, pass through and are projected into the eye. Normally, light enters the eyeball through the cornea and lens to be projected onto a single point on the retina.
Refraction measures the changes in direction of light rays entering the eye that cause the image not to be projected onto the retina, but to be projected in front of the retina (myopia), behind the retina (farsightedness) or at various points on the retina (astigmatism), causing vision problems.
Eye refraction problems are known as refractive defects and are not considered a disease but a visual disturbance. These defects are diagnosed through the ocular refraction examination, which is used to measure the prescription that a patient needs to correct a certain visual defect.
How is eye refraction performed?
There are two ways to perform an eye refraction:
- Objective refraction: It does not depend on the opinion of the patient.
- Subjective refraction: We collect data based on the subjectivity of the patient. That is, depending on how sharp the patient tells us that he sees based on the lens that we put on, we will obtain the refractive values.
objective refraction
By using a autorefractometer they are indicated by the refraction presented by the patient at that particular moment. This test is performed in the ophthalmological consultation and does not require eye contact with any external agent.
subjective refraction
The ocular refraction exam is a fairly simple procedure that we perform in the ophthalmological consultation. To perform the test, the patient must be seated in front of a special piece of equipment called phoropter, also known as a refractor.
The patient must look through the phoropter and focus on an eye chart located 6 meters away. The phoropter contains different lenses that the optrometry specialist will change until the patient indicates which of them he sees better with. The ideal is to choose the glass or the lens with which the eye chart is observed more clearly.
What pathologies does it detect?
The eye refraction exam helps detect vision defects, such as:
- Myopia: it is the defect that causes blurred vision of objects at a long distance because the light is projected in front of the retina, and not on it.
- Farsightedness: visual defect that causes blurred vision of images at close range because light from objects is projected behind the retina, and not on it.
- Astigmatism: this refractive defect is caused by an alteration in the curvature of the cornea that causes the light rays that enter the eye to be projected at various points on the retina at the same time.
- Presbyopia: over the years the crystalline lens, the natural lens of the eye, loses its elasticity and compromises its power of accommodation. This situation causes blurred vision at close range in all people from 40 years of age.
- anisometropia: is the difference in visual graduation between one eye and the other from 3 diopters that can cause complications in the fusion of images.