Carotid-cavernous fistula
La carotid-cavernous fistula, also known by her initials FCCIs a abnormal communication that is produced between the carotid artery and the cavernous sinus it can to extend anterogradely to orbit and cause significant damage to the eye structure.
The FCC can be provoked for various reasons, one of them being the skull fractures that cause tearing of the carotid artery.
There are two types of carotid-carvenous fistulas, the type direct that is of high flow, And the indirect, low flow. Early medical diagnosis of FCC is very important to take care of eye health and preserve, as much as possible, the correct vision of the patient.
Carotid-cavernous fistula
La carotid-cavernous fistula, also known by her initials FCCIs a abnormal communication that is produced between the carotid artery and the cavernous sinus it can to extend anterogradely to orbit and cause significant damage to the eye structure.
The FCC can be provoked for various reasons, one of them being the skull fractures that cause tearing of the carotid artery.
There are two types of carotid-carvenous fistulas, the type direct that is of high flow, And the indirect, low flow. Early medical diagnosis of FCC is very important to take care of eye health and preserve, as much as possible, the correct vision of the patient.
What is carotid-cavernous fistula?
The carotid-carvenous fistula is a abnormal communication between the carotid artery and the sinus carvenosus generating a arteriovenous pathology which develops in the direction of orbit seriously compromising eye health.
When this happens, the blood inside the vein arteriolizes and the intravenous pressure is altered, in such a way that it can change the pulsatility as well as the speed of blood flow.
Types of carotid-cavernous fistula
There are two different types of FCC, let's see:
Direct carotid-carvenous fistula
They are considered of high blood flow and are characterized by direct communication that is presented between the main trunk of the internal carotid and the cavernous sinus.
This type of FCC is associated with severe trauma with skull base fractures, surgical problems, rupture of carotid and intracavernous aneurysms, arterial problems and collagen deficiency.
Indirect-type carotid-carvenous fistula
Are low flow and are also known by the name of dural fistulae.

These fistulas cause a communication anomalous between the arteries of the meninge and the cavernous sinus. They occur spontaneously and are associated with factors such as Hypertension, intracranial surgery, sinusitis and pregnancy.
Approximately more than 50% of low-flow fistulae resolve on their own, while high-flow fistulae suggest embolization via intravascular catheters.
Causes
Carotid-cavernous fistulas are more common in women over 50 years of age who have a history of high blood pressure or who have suffered from this condition for many years.
All the causes that are recognized by the FCC are:
- Traumatic: such as those referring to head injuries.
- Spontaneous: such as congenital anomalies, ruptured aneurysms, collagen deficiency and arterial problems.
Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of carotid-cavernous fistula is very important for the patient's eye health. Whenever a person presents any head trauma, especially at the base of the brain, it is essential to evaluate eye health to rule out the formation of a carotid-cavernous fistula.
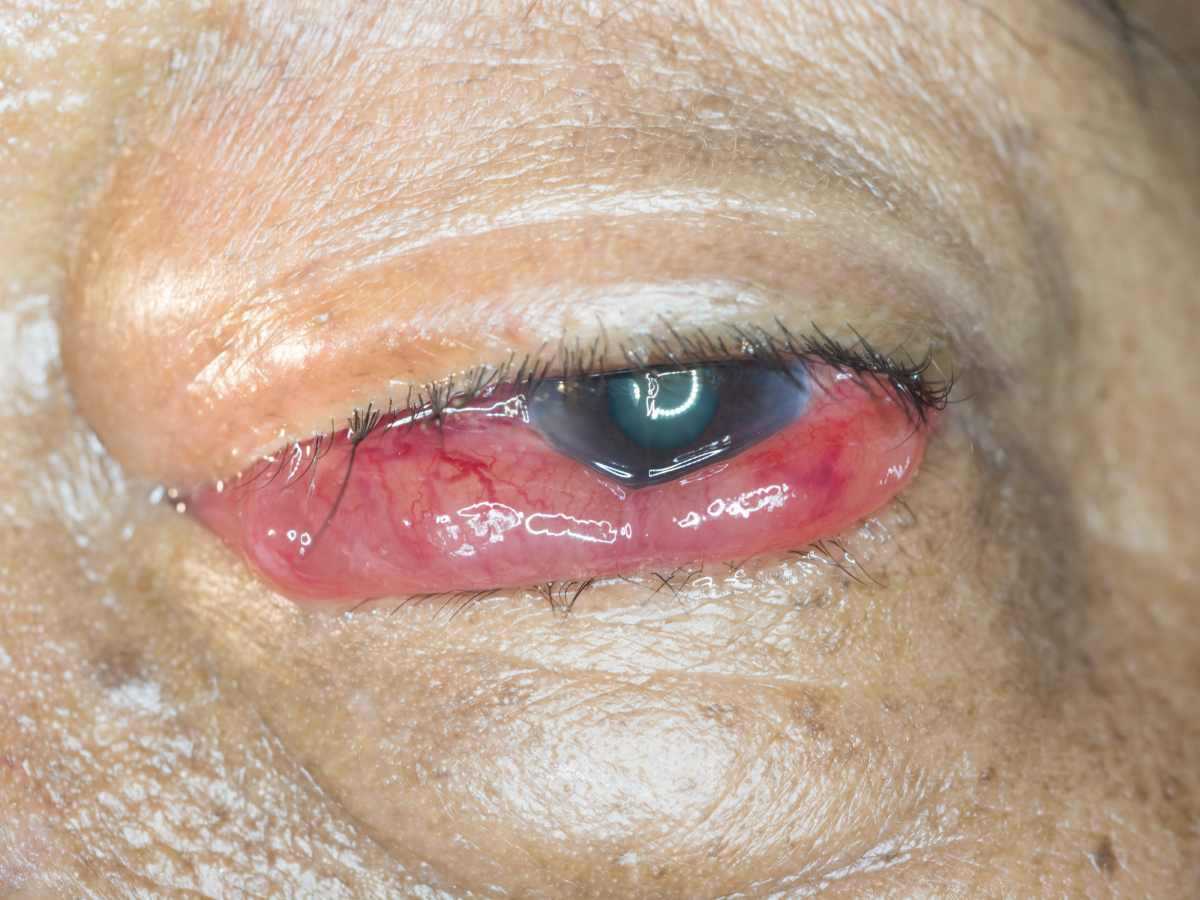
At the time of examining the eyes, the ophthalmologist should look for signs of loss in visual acuity, High intraocular pressure, exophthalmos, proptosis, chemosis o orbital breath.
For diagnosis, it will be necessary to Full review of the entire eyeball and perform a optical coherence tomography or OCT.
However, key tests for the diagnosis of this pathology are the arteriography and fluorescein angiography.
Carotid-cavernous fistula treatment
Treatment to treat carotid-cavernous fistula will depend on the type of fistula and how soon the diagnosis was made.
When the fistula is hintthat is to say low flow, it is usually advised maintain regular medical follow-up, since they usually resolve on their own and are considered a benign condition that does not affect the patient's vision.
All the direct fistulas, which are the ones associated with head injuries, specifically fractures at the base of the brain, are at higher risk and should be attended to immediately to prevent any eye damage.
In most cases, patients with this type of fistula are admitted to intensive care and with a delicate clinical picture.
The best way to treat this type of injury is by performing a embolization through intravascular catheters or endovascular balloon treatment.