The alteration in the perception of color, better known as discromatopsia, it is more common than we imagine. The visual system can discern colors thanks to the photoreceptor cells of the retina called cones. Any condition in these structures can affect vision.
Among the most common dyschromatopsies, the colorblindness, which is the inability of the ocular structure to identify certain colors such as red, green or yellow. This condition is hereditary, of genetic origin and affects more men than women. Because of this, many people wonder how a color blind person sees.
Do you know how a color blind sees? If you do not stop asking yourself, we invite you to discover it at Área Oftalmológica Avanzada.

What is it to be color blind?
The name colorblindness comes from John Dalton, a world-renowned chemist who had problems in the perception of color, therefore, all those with the same dyschromatopsia they are called color blind in honor of your research.
There are three types of cone cells and each of them is sensitive to a color: blue, green and red. The degree of involvement of a patient with color blindness can vary depending on the cones that are affected. Likewise, perception is affected well because these do not work normally or by its absence in the retina.
different types of dyschromatopsia or color blindness:
- protanopia or protanomaly.
- Deuteranopia or deuteranomaly.
- Tritanopia or tritanomaly.
How does a color blind person see?
To understand how a color blind sees, it is important to understand how the visual system works. Light that penetrates from the outside is projected onto the retina, the sensitive tissue that contains the rods and rods. Later, that light is transformed into a nerve signal that travels to the brain through the optic nerve. The brain interprets the received signals and converts them into images.
To the question: how does a color blind person see ?, we can say that the vision of these patients may vary depending on the degree and type of dyschromatopsia you suffer, for example:
- Dichromatism: there may be a problem perceiving the color red, green and less frequently blue.
- Trichomaticism: is a mild version of dichromatism and the most common type of color blindness. The patient perceives the altered primary colors. The symptoms are the same as those present in dichromatic color blindness but with less intensity.
- Monochromatic- This condition is rare and occurs when only one type of cone works on the retina. It is usually accompanied by other vision problems, such as sensitivity to light.
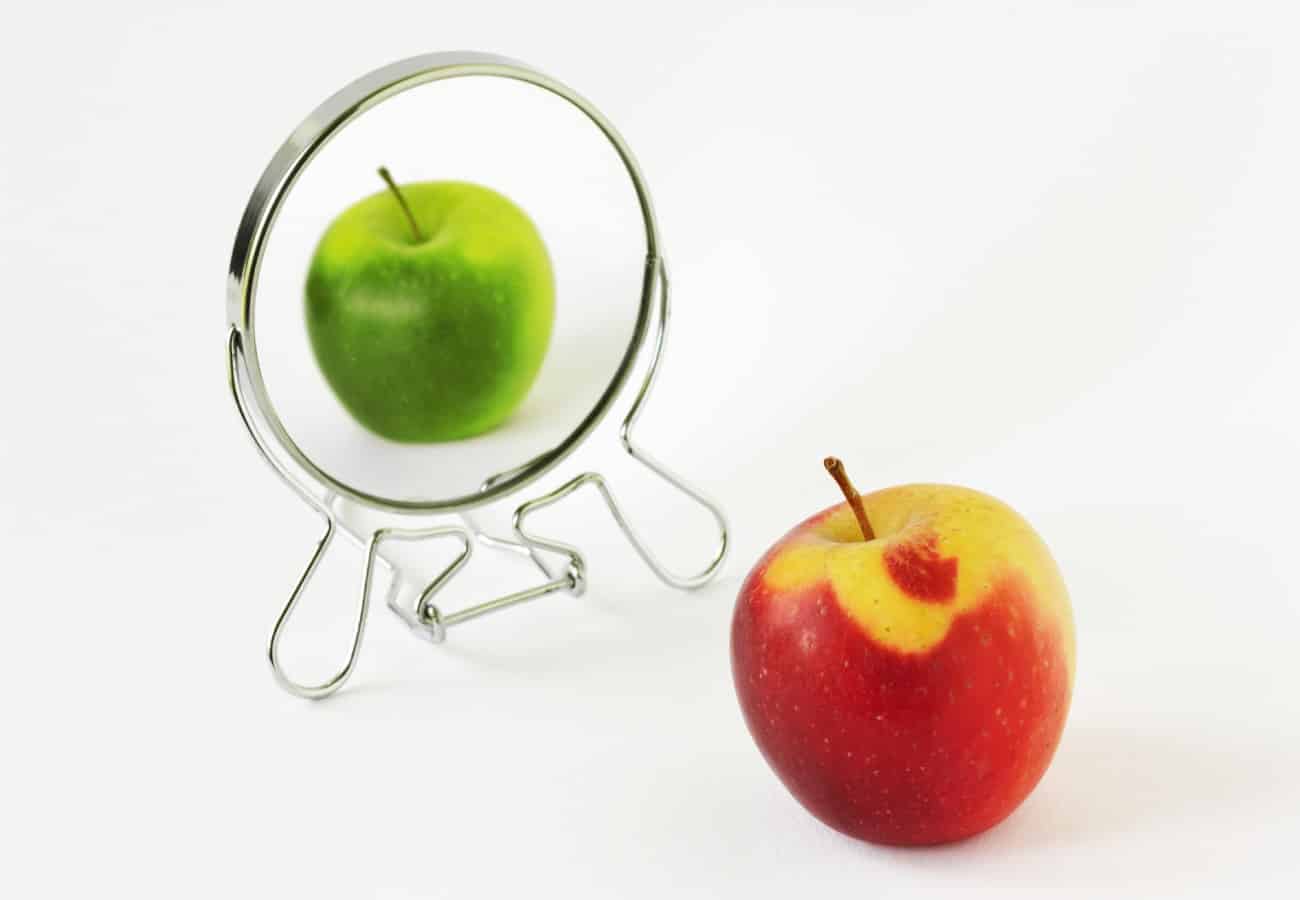
Many people wonder how a color blind person sees the colors of the traffic light, due to his inability to see the colors green, red and yellow correctly. The truth is that they see it normal. Why? Because the problem of people with dyschromatopsia occurs when they have to distinguish colors from the same range, not when they have to discern opposite tones.
A color blind person will never have a problem distinguishing the colors red, yellow and green from a traffic light. The problem occurs, for example, when they have to differentiate the different shades of green in a forest. Therefore, your vision has limitations in the ability to discern between similar colors.

What colors do colorblind confuse?
As we explained earlier, the big problem with people with color blindness is that they tend to confuse colors. They do not distinguish the ranges of red, green and yellow. It can even be difficult for them to differentiate a brown tone from some variants of red.
Few patients with color blindness present limitation to identify blue variations.
Is it possible that you don't see any color?
Yes, there are people who have an inability to see all colors. This condition is not a type of color blindness and is known by the name of achromatopsia.
Achromatopsia is defined as the color blindness and it occurs because the retina is absent of the three types of cone cells. In this case, the condition is severe and the person has inability to distinguish the colors of the traffic light.
How do you know if you are color blind?
Most color blind suffers from this condition from birth and therefore they may not know that their vision is different. If in your family there is a history or suspicion that you may have a problem in the perception of colors, the best thing you can do is go to the ophthalmologist.
To determine if you are color blind, one of the tests we perform the most is the Ishihara test. This test consists of looking at 38 cards and saying what you see in each of them. The cards are designed with dots of different ranges of colors, which form a number. People with normal vision see different images than those with dyschromatopsies.
Have we clarified how a color blind person sees? If you still have doubts or suspect that you suffer from any of these problems related to the perception of colors, do not hesitate to contact us. In Área Oftalmológica Avanzada We have ophthalmologists who are experts in color blindness and we are happy to assist you.




Excellent explanation. Thank you so much.
For occupational physicians, this reference is very useful.
I congratulate you amply.
Dr Ruben Olivier